Receptor Types
Dublin Core
Title
Receptor Types
Subject
Receptor Types
Description
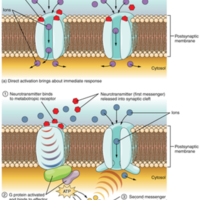
(a) An ionotropic receptor is a channel that opens when the neurotransmitter binds to it. (b) A metabotropic receptor is a complex that causes metabolic changes in the cell when the neurotransmitter binds to it (1). After binding, the G protein hydrolyzes GTP and moves to the effector protein (2). When the G protein contacts the effector protein, a second messenger is generated, such as cAMP (3). The second messenger can then go on to cause changes in the neuron, such as opening or closing ion channels, metabolic changes, and changes in gene transcription.
Contributor
Cut Rita Zahara
Rights
Creative Commons
Type
Image
Files
Collection
Citation
“Receptor Types,” Open Educational Resource (OER) - USK Library, accessed May 23, 2025, http://202.4.186.74:8004/oer/items/show/1176.